BJUT and H.E.L. Joint Laboratory-Collaborative Excellence for a Bright Future
By the end of 2023, the number of new energy vehicles in China reached 20.4 million; whether it's power batteries or new energy vehicles, China accounts for more than 60% of the global share. As the industry rapidly develops, the safety of batteries has increasingly become a focal point of concern. Since its establishment in 1987, the British company H.E.L Group (H.E.L) has been providing process optimization and reaction hazard assessment solutions for various industries. Alongside the vigorous development of China's new energy industry, H.E.L has provided outstanding battery safety solutions for hundreds of clients and is collaborating with leading research units to innovate, offering more reliable system solutions for the battery, chemical, pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and petrochemical industries.
On September 24, 2024, Ms. Louise Madden, CEO of H.E.L Group, visited the Joint Laboratory of Lithium-ion Battery Thermal Safety and Control Technology at the School of Mechanicall and Energy Engineering, Beijing University of Technology. Antpedia interviewed Ms. Louise Madden, Professor Ji Changwei, a doctoral supervisor from the Department of Automotive Engineering at Beijing University of Technology, Mr. Allen, General Manager of H.E.L Group China, and Dr. William, Chief Application Expert of H.E.L Group China. Through the exchange and collision of ideas, these experts will show us the technical trends in battery testing and process safety, as well as the prospects for future innovation through collaborative research and development.

Professor Ji Changwei, professor of Automotive Engineering of Beijing University of Technology (third from the right), Ms.Louise Madden (third from the left), CEO of H.E.L Group, Mr. Allen (second from the left), General Manager of H.E.L Group China, and Dr. William (first from the left), Chief Application Expert of H.E.L Group China
H.E.L: Health, Safety, and Sustainable Development Strategy
Louise first introduced H.E.L's development strategy. H.E.L focuses on innovation, sustainable development, and close cooperation with customers, concentrating on key industries related to net-zero emissions. Louise stated that H.E.L aims to continuously advance solutions in battery testing, biotechnology, and semiconductors to address global challenges such as climate change, waste management, sustainable energy, and energy storage.
In the field of battery testing, H.E.L's main market is China, and it is expanding to India, the United States, and Europe. H.E.L has also developed a series of solutions to improve the safety and performance of energy storage systems, thus opening up new markets for the company's products.
In the field of biotechnology, the BioXplorer series of desktop parallel bioreactors have unique high-pressure processing capabilities, which can produce alternatives to fossil fuels, treat wastewater, and be applied to different fields.

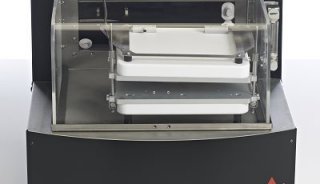
BioXplorer 400P | High-pressure desktop, parallel 4 bioreactor platform
In the semiconductor market, H.E.L products have shown tremendous potential, from using existing fine chemical solutions for offline or in-situ measurement of circuit boards and components, using new products such as the iso-BTC e isothermal calorimeter. H.E.L’s products provide a comprehensive system solution for the semiconductor market.

iso-BTC | Desktop, Small Thermal Power, Small Battery, Battery Thermal Performance Testing, Isothermal Calorimeter
"We are integrating artificial intelligence with H.E.L's unique control software to further improve our customers' R&D efficiency," Louise said. "Last year, we also established more customer training centers to improve global customer satisfaction, including successful training courses held in China and India."
Joint Laboratory ?-Cooperation and Win-Win situation
Regarding the joint laboratory, Mr. Allen, General Manager of H.E.L Group China, introduced the opportunity for cooperation between the two parties and the projects H.E.L will undertake; Dr. William, Chief Application Expert of H.E.L Group China, talked about the technical support for the joint laboratory; Professor Ji Changwei, a doctoral supervisor from the Department of Automotive Engineering at Beijing University of Technology, put forward suggestions and prospects for the future cooperation and development of the joint laboratory.
Mr. Allen detailed several aspects of the cooperation between H.E.L and Beijing University of Technology. First, the joint laboratory will serve as the Beijing Technology Center, providing professional technical support and training services for H.E.L's customers. It will act as an academic cooperation platform to undertake horizontal scientific research projects.
The opportunity for cooperation is based on Beijing University of Technology's research characteristics in the energy industry, especially its academic focus on electric vehicles and battery fields, which aligns with H.E.L's business development needs. H.E.L hopes to leverage the university’s research advantages to empower the Company's products and provide professional technical support for customers. For the future, Mr. Allen expressed his expectations for the cooperation laboratory, which will provide technical services and training support for H.E.L's more than 130 BTC calorimeters customers in China.
Talking about the technical support for the joint laboratory, Dr. William introduced two points.
First, the company provides regular daily maintenance and operation training to ensure the normal operation of laboratory equipment; for experimental data analysis, it provides personalized program rewriting services.
Dr. William emphasized the importance of the five major elements "man, machine, material, method, and environment" in experiments, that is, personnel, equipment, materials, methods, and environment. H.E.L is committed to ensuring stable equipment performance and advocating for the standardization of experimental methods. The company's annual training sessions not only involve equipment principles and maintenance but also include the unification of experimental methods such as experimental calibration, sample preparation, and placement, ensuring the accuracy and repeatability of experiments.
In addition, H.E.L also provides data analysis training, teaching researchers how to plot charts, interpret data, and provide possible solutions for specific problems. Through continuous communication with customers and experience accumulation, H.E.L helps researchers troubleshoot problems and improve the success rate of experiments.
Secondly, another important goal of the joint laboratory is to promote academic collaborations with industry. H.E.L hopes to strengthen connections with the academic community through the laboratory, promote the standardization of testing methods and personnel training, achieve data sharing and comparability, and avoid unnecessary repetition of work and wasting of resources.
Talking about the significance and expectations for the future of the joint laboratory, Professor Ji said: First, customer service and technical support are very important. Second, the exchange in cooperation and solving challenging problems can promote product innovation, such as improving product performance to meet cutting-edge needs, and diversifying and modularizing development to meet the needs of more levels of customers in the market. Third, the joint laboratory can promote the transformation of scientific research results, promote the real-life application of new technologies, and ultimately achieve deep integration of academic research and industrial development through a win-win cooperation model. Fourth, it can cultivate more professional talents.
"I hope the laboratory can become a comprehensive platform integrating technological innovation, talent training, academic exchange, and industrial services," said Professor Ji, looking forward. "I hope we work together to build the cooperation laboratory into a leading institution in the fields of battery safety, performance testing, and new energy technology, making an important contribution to sustainable social development."
Pioneer in Battery Safety Research
Professor Ji's research group has three main research directions: hydrogen and hydrogen hybrid fuel piston and rotary internal combustion engines, internal combustion engine waste heat utilization and numerical simulation; thermal management, thermal safety, and environmental recycling of power lithium-ion batteries; and performance optimization and thermal management of fuel cells.
With 20 years of experience in hydrogen internal combustion engine research, Ji Changwei joined the Beijing Electric Vehicle Expert Committee, focusing on battery recycling technology and establishing a battery recycling demonstration base in Huailai. "Of course, breaking a glass and making a new glass from the broken pieces is definitely more expensive than a new glass," said Professor Ji Changwei, using a metaphor. "Currently, the price of lithium carbonate has dropped too much, so battery recycling does not have much commercial value, but it is an environmental cause that must be strongly supported by the government."
Starting in 2012, the research group began to study lithium battery safety and purchased and built safety measurement devices. For example, the research group has been using H.E.L's calorimeter series products and designed and built a battery high and low temperature test bench, using high-speed cameras to observe and study the combustion process and fire extinguishing efficiency of batteries.
The research group has achieved many results in the field of batteries, participating in key national research and development plan projects such as "Sub-topic: Research on Thermal Management Technology of Electric-Electric Hybrid System for Fuel Cell Sedans" and the National Natural Science Foundation of China's general project "Research on Mixture Formation, Combustion Mechanism, and Control Strategy of Hydrogen-Oxygen Rotary Engine (51976003)". It has also carried out cooperative projects with many well-known enterprises and universities, including Tianjin Lishen, BYD, FAW, Beijing Institute of Technology, and University of Science and Technology Beijing.
The focus of the research group is to develop a battery safety early warning system, predicting and preventing possible battery thermal runaway events by establishing a thermal safety model. Their innovative method combines experimental data with numerical simulation, effectively reducing the dependence on a large number of sensors, reducing costs, and improving the accuracy and reliability of the early warning system. In addition, the research group is also actively exploring the research of new generation battery technologies such as solid-state batteries and sodium batteries, and is committed to further enhancing the ability of battery system safety early warning test through the combination of experiments and numerical simulation.
Thermal Runaway Mechanism ?-The important role of the calorimeter
Professor Ji then briefly introduced the specific mechanism of thermal runaway of lithium-ion batteries under overcharging conditions; and compared the differences in thermal safety performance of different chemical systems of lithium-ion batteries (such as NCM, LiFePO4) under overcharging conditions. He pointed out that overcharging will cause an increase in the internal current of the battery, generating a large amount of heat. When the internal temperature of the battery rises to a certain extent, it will trigger the phenomenon of thermal runaway. LiFePO4 batteries usually first smoke when overcharged, and less likely to catch fire, which is attributed to their lower energy density and higher thermal runaway starting temperature. In contrast, NCM has poorer thermal safety under overcharging conditions, and they may undergo thermal runaway at lower temperatures, and the reaction is more intense.
Under normal circumstances, lithium ions can pass through the battery interior in an orderly manner, but under overcharging conditions, the electric field drives lithium ions to migrate in a scramble, causing damage to the internal structure. He explained that overcharging leads to the deposition of lithium ions on the surface of the anode to form dendrites, which may pierce the separator and cause an internal short circuit, ultimately leading to battery thermal runaway.
Understanding thermal runaway makes the issue of battery safety particularly important.
In the field of battery safety research, calorimeters are key tools that can delve into the thermal runaway phenomenon of lithium-ion batteries under overcharging conditions. Adiabatic calorimeters can maintain a state close to adiabatic during the battery heating process, thereby accurately capturing the battery's own exothermic reaction. By slowly increasing the temperature and carefully controlling the temperature gradient, researchers can monitor the entire process from the initial reaction to the violent reaction, thereby identifying the critical point of battery thermal runaway.
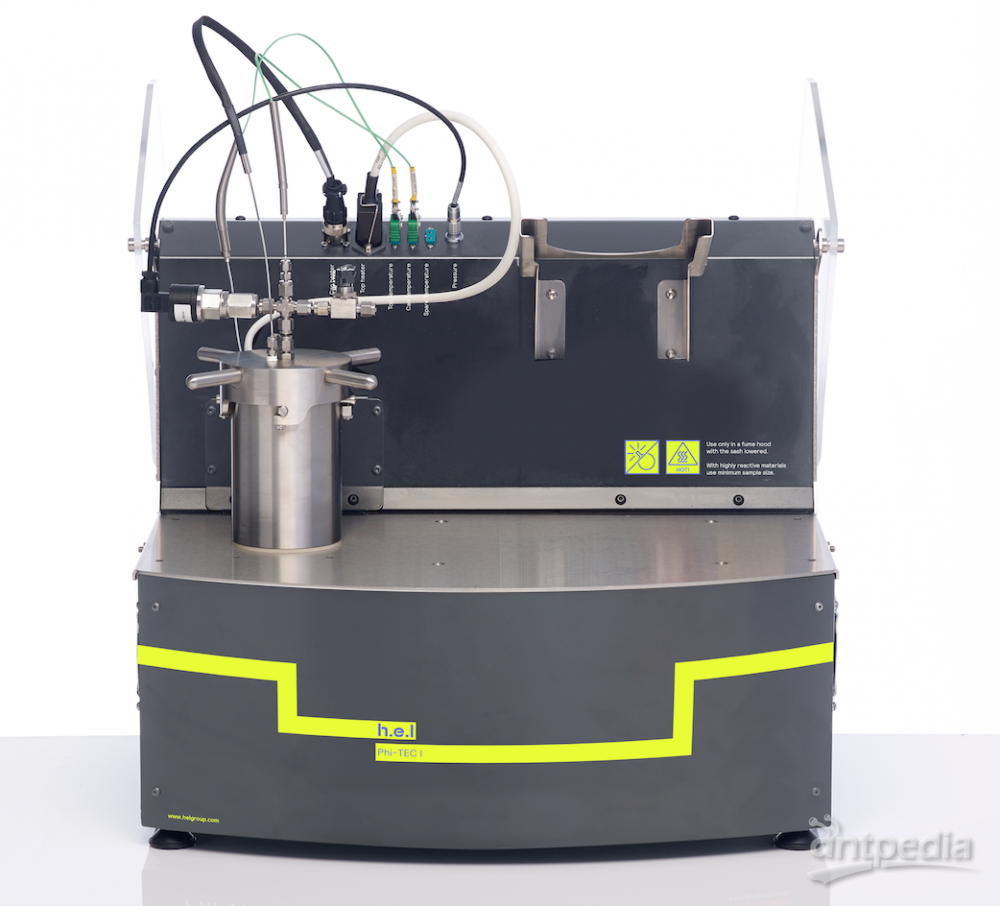
Professor Ji pointed out that adiabatic calorimeters can help determine the safe temperature of batteries to ensure their safe use. In the joint laboratory, we saw a BTC-130 adiabatic calorimeter and a BTC-500 floor-standing adiabatic calorimeter.

BTC-130 | Desktop, Small-sized Battery, Small-capacity Battery, Material Level, Battery Thermal Performance and Safety Performance Testing, Adiabatic Calorimeter

BTC-500 | Large-sized, Large-capacity, High-activity System, Battery Thermal Performance and Safety Performance Testing, Floor-standing Adiabatic Calorimeter
In the experiment, calorimeters also combine physical methods and camera technology to analyze the flame characteristics during the battery combustion process, including the height, length, area, and color of the flame. These physical data combined with the temperature measurements of the calorimeter provide a more comprehensive perspective on battery thermal runaway.
Professor Ji expressed his firm trust and satisfaction with H.E.L's products in the interview, sharing his 12 years of experience using H.E.L equipment, and praised the reliability and durability of the products, as well as the service capabilities of the engineers. Professor Ji also made some suggestions for product development and innovation: a larger visible window and camera, more modular parameters, more sensitive sensors to achieve precise temperature with smaller gradients, and faster measurement speed. "These improvements will better meet the market's demand for high-end scientific instruments and help promote H.E.L's continuous innovation and long-term development."
Thermal Calorimetry Technology Development Challenges and Trends
For the application of battery insulation thermal technology in the field of lithium ion battery safety and its challenges. He pointed out that the core of this technology is to accurately capture the initial temperature point of battery thermal runaway, rather than just monitoring the moment when thermal runaway occurs.
"We face one of the challenges of how to improve measurement accuracy and how to make the equipment capable of withstanding higher pressures and temperatures," said Professor Ji when talking about technical difficulties. "We hope that calorimetric equipment can adapt to larger-sized batteries, have stronger pressure and temperature resistance, and be able to measure more parameters, providing more powerful experimental data to support the safety design and optimization of batteries."
"At present, domestic calorimetric technology mainly serves the thermal characteristic testing of explosives and dangerous goods," Professor Ji said, expressing more expectations for H.E.L. "In terms of heat and temperature testing, the UK has more accumulation and advantages in sensors, which can develop more sensitive sensors to achieve precise temperature control and measurement with smaller gradients; in component measurement, it can adopt more measurement technologies to measure more parameters."
Comprehensive Solution to Empower the Industry
H.E.L provides a series of innovative core instruments in the fields of battery and chemical thermal-related research, including BTC-500, BTC-130 adiabatic accelerated calorimeters for measuring battery stability; iso-BTC, iso-BTC + isothermal calorimeters for measuring battery heat generation performance, etc. Louise said that the above equipment covers from desktop to larger scales, destructive and non-destructive battery testing needs, thereby helping users develop safer and higher-performing battery products.
Dr. William introduced H.E.L's calorimeter products in detail.
The BTC series is based on the Phi-tec product launched in 1989, using an improved adiabatic control model that controls the chamber temperature according to the sample temperature change, achieving adiabatic control of the reaction process. After 2000, with the gradual development of lithium-ion batteries, the company launched the iso-BTC product, mainly for measuring the heat generation power of batteries. The principle is to use the compensation adjustment of the compensation heating plate to measure the heat generation of the battery. This method does not require the use of heat flux calorimeters, reducing the cost of use, and can measure larger heat generation.
H.E.L's products are all based on the same control platform, and only by changing the control drive and configuration file can different test platforms be quickly switched, reducing the internal R&D costs of H.E.L and also facilitating users to learn different test equipment and methods.
Since it is based on the same test platform, the development process for test methods is the same, and the test methods can be defined according to user needs. For example, the development of test methods for energy storage batteries national standards is designed by H.E.L's engineers based on file descriptions. Recently, some customers need to add delay judgment functions to the test process, and H.E.L's engineers have added new test judgments according to customer needs. This flexible test method establishment process provides more possibilities for users. Since this test method requires users to organize test logic and control points, it can encourage users to think more deeply about test needs and processes, allowing users to become professionals in the field.
In terms of equipment, H.E.L has reserved multiple interfaces for users to develop on their own or for third-party development. For example, in order to increase the heating power of the sample, a third-party company has developed an amplifier to improve the sample's heating rate and reduce the user's test time. For another example, a third-party company has developed a mass spectrometry joint solution for real-time gas analysis during the material and battery testing process. H.E.L welcomes collaborations to support the development of new products to add value to users.
In China, for China
Dr. William said: In China, H.E.L's products cover a wide range of industries and applications, mainly serving institutions and enterprises that need to conduct thermal measurement and safety assessment of chemical products, including chemical safety research institutes, chemical product manufacturers, battery manufacturers, host factories, third-party testing agencies, and universities, etc. H.E.L's products are applied to key areas such as battery testing technology, process safety, chemical synthesis, and biological process development.
In terms of after-sales service for Chinese customers, H.E.L has the following measures:
First, respond to customers within 24 hours of reporting a repair; provide free after-sales service for customers within the warranty period, and provide instrument maintenance solutions for customers out of warranty.
Second, all after-sales engineers have high education and chemical-related backgrounds.
Third, it is recommended to use original factory parts, and H.E.L has parts warehouses in Beijing and Jiangsu to respond to customer needs more quickly.
Fourth, provide special equipment usage training after equipment installation, with at least one application technology training session every year, including battery testing, relief safety training, etc. The training invites experts from the headquarters, domestic experts, and scholars to share knowledge and experience, discuss problems together, and help H.E.L’s customers gradually become professionals in the corresponding fields.
Fifth, establish a global information sharing platform to share application information in different fields, and continuously improve the application and technical updates of equipment.
Sixth, develop methods for Chinese customers. For example, if customers need to improve test methods, the H.E.L China team will discuss the test plan with the customer to understand the customer's test needs, and then establish new test methods based on H.E.L's independently developed test platform. Currently, it is mainly done through remote operation of the computer to establish and edit test methods, which solves user problems while reducing the communication and operation costs of both parties, achieving a win-win for customers and H.E.L.
"A customer said that is like Android, open and," said Dr. William. "H.E.L provides a large number of operation interfaces that can help customers achieve many functions, including gas collection during the test process, pressure monitoring during the test process, and linkage with domestic main charging and discharging equipment. For example, H.E.L has achieved online analysis of the liquid phase reaction process using Raman; it is developing and verifying online mass spectrometry gas analysis. After verification, it will be of great significance for understanding material reaction processes under high pressure and special application scenarios such as thermal runaway of lithium-ion batteries. These analysis results can ultimately be implemented in early warning or safety protection for working conditions."
Louise added: "We are very pleased that Dr. William has joined H.E.L, and are grateful for the support his team has brought to Chinese customers. We also recently welcomed Professor Du as our Chief Scientific Advisor. We hope that Chinese users will participate in H.E.L's annual company meeting to stimulate more knowledge sharing. We just held the Phitech process safety equipment technology training, and Dr. Derek, who worked at AGL (Australian Power Company) for more than 30 years, shared his many years of knowledge and experience as a lecturer for the Chinese team and Chinese users. These measures help us establish deeper customer relationships."
Accelerating Two Major Businesses to Support Young Teams to Achieve Better Results
Regarding the recent development of H.E.L China, Louise talked about three points.
First, since the establishment of H.E.L China in China in March 2020, H.E.L's business in China has achieved rapid growth and has accumulated profound professional knowledge and technical strength in the field of battery testing. "We are the market leader in China's battery testing, positioning us as a global leader in this field, so battery testing is an area that H.E.L will continue to invest in," said Louise.
Second, actively expanding the application in the semiconductor industry. From using existing fine chemical solutions to using new products such as the iso-BTC e isothermal calorimeter, H.E.L provides a comprehensive system solution for the semiconductor market.
Third, ongoing increase in investment in China with the anticipation that the business will continue to grow significantly over the next few years. Louise said: "A lot of H.E.L's business comes from China, and I am very proud to work with the Chinese team, who have performed very well. I enjoy coming to China to see what the team is doing and support them in achieving success."